List Data
Last Updated: 16 Jul 2021Introduction
This article describes how lists work, what the actions, conditions and expressiosn related to Reading List do and what types of lists you can build. This involves the following actions, conditions and expressions:
| Actions | Conditions | Expressions |
|---|---|---|
 |  |  |
Types of List Data-Structure
Lists must be defined into a specific structure. You can use the BASIC "Write Data-Custom" action to build this structure manually, or in case of Object Type Lists use the PRO "Append List-Data" action to append data at the back of the list.
| Object-Type List | Value-Type List |
|---|---|
This List type is hugely scalable, has more advanced capabilities (query sort, order, filter) and lots of data can be stored. The data structure must be in the following format: 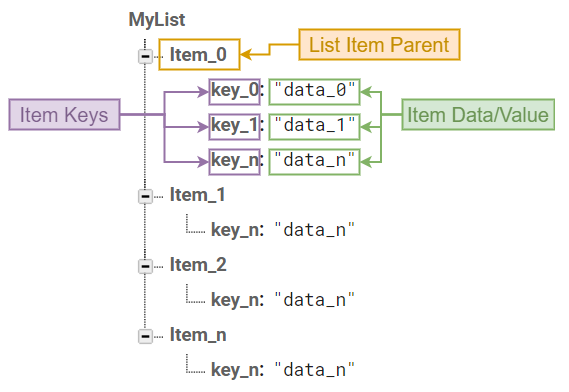 Here, each Item Parent is actually a JSON object which can contain Keys and Data. This type of list can be used for building chats, posts, friend management, leaderboard, etc. | This List type can contain limited data but can be a huge data saver, and easy to use 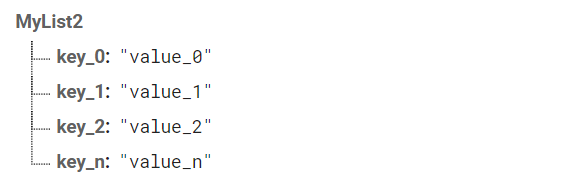 Value-type list querying is only relevant if your items are just values and not JSON objects. |
Actions
Append List-Data • [Category: Write]
This is only for Object-Type Lists.
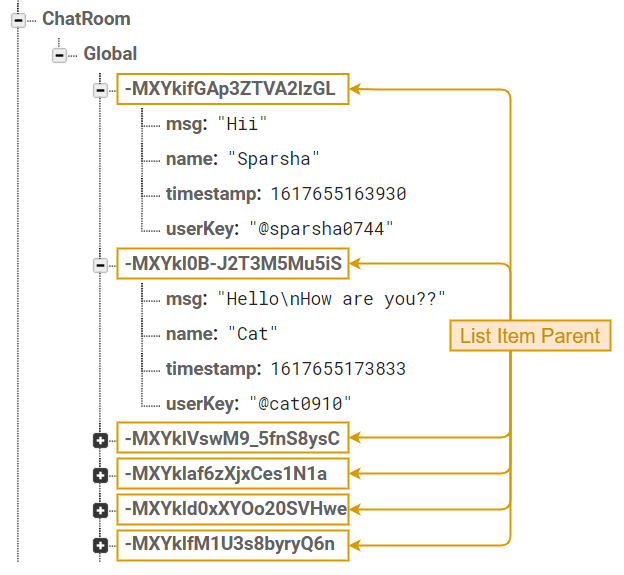
Use this action to append data to a list in multiuser applications. This action generates a unique Item Parent Key every time a new item is added. By using these auto-generated keys for each new element in the list, several clients can add Items to the same location at the same time without write conflicts. The unique key generated by this action is based on a timestamp, so list items are automatically ordered chronologically.
The image in the below shows the structure of a Chat Room. Note the Item Parent Keys generated by the "Append List-Data" action:
Read List-Data • [Category: Read List]
This action will start the list reading or fetching process. (You must be familiar with similar actions in the BASIC Plugin such as the "Read Data-User Account" and "Read Data-Custom".)
There are init options for this action which can be used to request sorted and filtered data.
PARAMETERS:
-
Sync When :list:(1)Specify a method on when to sync. The "On List Change/Read" (6) condition will trigger according to the sync method chosen. Disabling Sync will mean "On List Change/Read" (6) condition will read only once when the list has been loaded successfully for the first time.
-
Get Reversed :checkbox:
If this is enabled, you will get the requested data in reversed order. This can be used with "Limit to Last" Init Option to get data in descending order. -
TagArray Key :string:(Object Type List only) (2)Specifying this will Auto-format the Tags found in this message Key and also store an array of all user tags in the
tagUserKeyArrayexpression.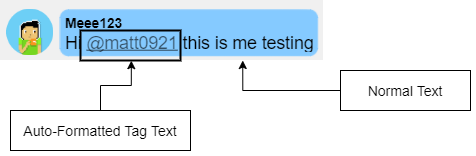
Init Read List Actions • [Category: Read List]
Initializing can make the "Read List Data" Action to request sorted and filtered data.
If you want to Initialize your "Read List Data" Action, "Init Read" actions must be specified before each "Read List-Data" action. If you do specify any init options to initialize your "Read List-Data" action, the list you will get will not be filtered, and ordering of data will depend on the Lexicographic Order of Key Names..
Multiple initialization actions can be used for a "Read List-Data" action. But using the same option twice or more will overwrite the previously set options.
There are six initialization actions:
-
This action is used to specify which value should be used to order the list by.Init Read: 1.Order ByPARAMETERS:TIP & TRICKFirebase RD always gives us the data in ascending order. Use "Limit To Last" Init option and enable "Get Reversed" option in "Read-List Data" Action to get the data in descending order.
-
Specifies the ordering method to be used. There are three types of ordering methods:Order Method :list:(3)- Order by Item Key Data (Object-type) - This will order the list according to the data stored in an Item Key. This data in the database must be a string or a number.
- Order by Parent Key Name (Object-type) - This will order the list according to the Parent Key Name.
- Order by Value (Value-type) - This will order the list according to the value of keys in a Value-type list.
Item Key Name :string:
If you have selected "Order by Item Key Data" as your Order By Method, you need to specify this. This specifies the Item Key by the data of which your List will be ordered.
-
-
This action is used to specify the maximum number of items to read from the beginning of the list stored in database.Init Read: 2.Limit to First(4)
PARAMETERS:Limit to First :number:
The maximum limit
-
This action is used to specify the maximum number of items to read from the end of the list stored in database.Init Read: 3.Limit to Last(5)
PARAMETERS:Limit to Last :number:
The maximum limit
-
Get List items greater than or equal to the specified data.Init Read: 4.Start Read at/after�PARAMETERS:noteThis specified data/value depends on the "Order By" Method (3) chosen.
Method :list:- Start At - Get items greater than the specified data/value
- Start After - Get items greater than/equal to the specified data/value
Value :string/number:- Value to compare the specified data/value with
-
Get List items less than or equal to the specified data.Init Read: 5.End Read at/beforePARAMETERS:noteThis specified data/value depends on the "Order By" Method (3) chosen.
Method :list:- End At - Get items lesser than the specified data
- End Before - Get items lesser than/equal to the specified data
Value :string/number:- Value to compare the specified data with
-
Get List items equal to the specified data.Init Read: 6.Get Items Equal ToPARAMETERS:noteThis specified data/value depends on the "Order By" Method (3) chosen.
Value :string/number:- Value to compare the specified data with
Conditions
➜ On Append/Write/Replace • [Category: Write]
This is triggered when any Write action such as append, write or replace is completed.
➜ On List Change/Read (6) • [Category: Read-List]
This is always triggered when any list has been read successfully.
Also, if "Sync When" is enabled in "Read List-Data" (1) Action, "On List Change/Read" Condition is triggered according to the Sync method chosen.
➜ On Reach List End • [Category: Read-List]
This is triggered when the length of list read is less than the maximum length limit specified in Init Actions: "Limit to First" (4) and "Limit to Last" (5)
Has Reached List End • [Category: Read-List]
This is the same as the previous one except that this one is a non-trigger condition.
True when the length of list read is less than the maximum length limit specified in Init Actions: "Limit to First" (4) and "Limit to Last" (5)
Expressions
getTagsFromString • [Category: List: Both List Types]
Firebase RD Pro Plugin has the options to create and read UserKeys which usually look like userkeyname@0000. An user can tag another person by including his/her UserKey Tag in the stored data. This can be used in a Chat system to Tag users in a message.
The Tags stored in a string data must follow this markup format: "/@userkeyname0000/". (The slashes "/" are important)
The "getTagsFromString" expression accepts a string parameter and then returns a JSON-Array-string of all Tags found in that string.
tagUserKeyArray • [Category: List: Object-Type]
Get an array string of tagged users in a list item when TagArray Key (2) is mentioned in Read List-Data Action.
The tags stored in the string data must follow the above mentioned markup format.